What is a Conductor?
A conductor is a material that allows electric current to flow through it. Conductors are mainly used to transmit electrical energy in wires, cables, transmission lines, and electrical machines. Common examples of conductors are copper, aluminium, and silver, which are widely used in power systems and electrical installations.
Types of Conductors
- All Aluminium Alloy Conductor (AAAC)
- All Aluminium Conductor (AAC)
- Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced (ACSR)
- Hard-Drawn Copper Conductor (HDC)
- Aluminium Conductor Alloy Reinforced (ACAR)
- Galvanized Steel Conductor
- Cadmium Copper Conductor
- Phosphor Bronze Conductor
- Zinc-Coated Steel Conductor (Shield Wire)
- Bundled Conductors (for Extra High Voltage lines)
1. Hard-Drawn Copper Conductor (HDC)
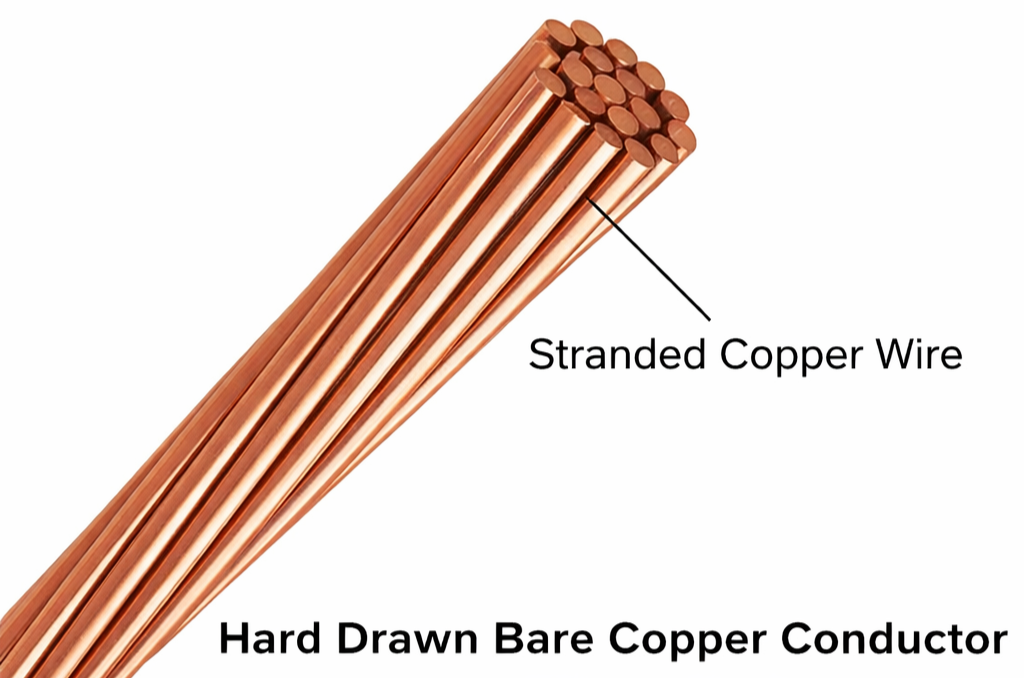
Hard-drawn copper conductors were widely used in early transmission systems because of their excellent electrical conductivity. They provide low resistance and high current-carrying capacity. However, their heavy weight and high cost limit their use in modern long-distance transmission. Today, they are mainly used in short spans and special applications.
2. All Aluminium Conductor (AAC)
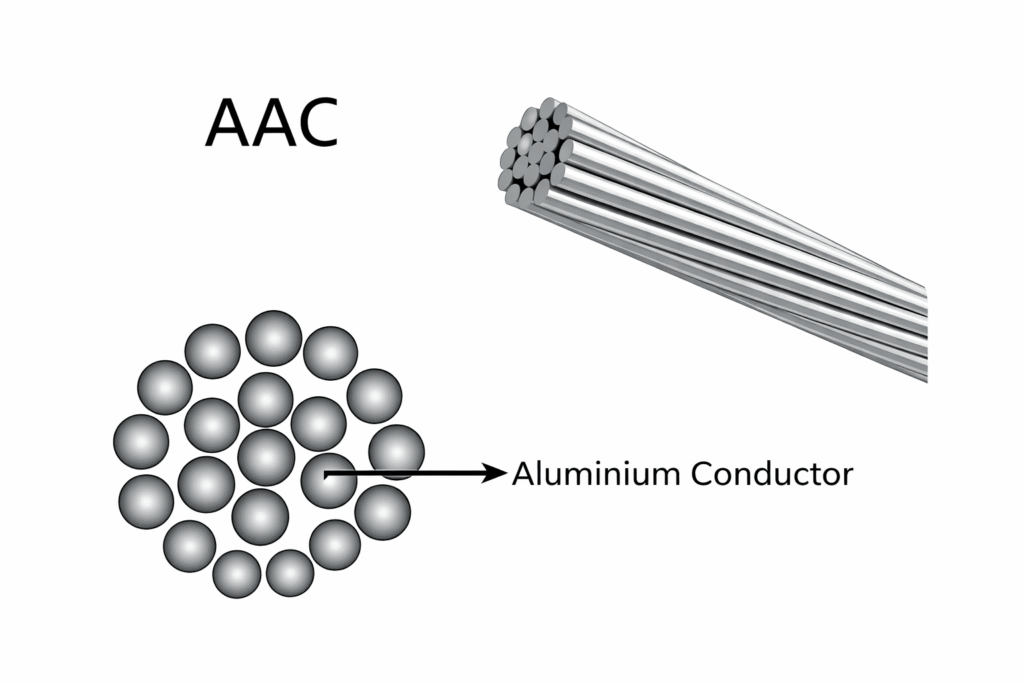
AAC is made of pure aluminium strands twisted together. It offers good conductivity but low mechanical strength, making it suitable only for short spans. These conductors are commonly used in urban distribution networks and low-voltage transmission lines. AAC is light in weight and easy to install.
3. All Aluminium Alloy Conductor (AAAC)
AAAC is manufactured from aluminium alloy to improve tensile strength and corrosion resistance. It is suitable for medium-span transmission lines and for use in coastal or polluted environments. These conductors provide better durability than AAC while maintaining reasonable conductivity. AAAC is widely preferred in corrosive areas.
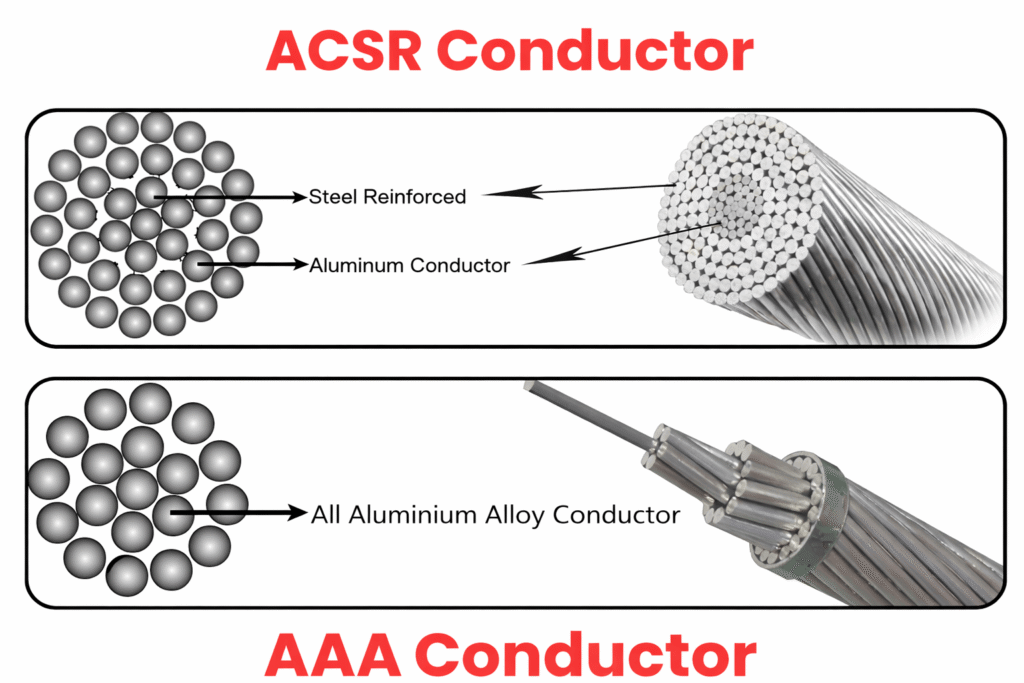
4. Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced (ACSR)
ACSR consists of aluminium strands surrounding a steel core to provide very high mechanical strength. The steel core carries mechanical load while aluminium conducts current. It is the most commonly used conductor for long spans and high-voltage transmission lines. ACSR performs well under heavy wind and ice loading conditions.
5. Aluminium Conductor Alloy Reinforced (ACAR)
ACAR combines aluminium strands with an aluminium alloy core to achieve both high conductivity and good mechanical strength. It provides better electrical performance than ACSR and higher strength than AAC. ACAR is used in heavily loaded transmission lines and long spans where both strength and current capacity are required.
6. Galvanized Steel Conductor

Galvanized steel conductors possess very high tensile strength but poor electrical conductivity. Therefore, they are rarely used for carrying power. They are mainly employed as earth wires, guy wires, and support conductors in transmission systems. Their primary role is mechanical support and lightning protection.
7. Cadmium Copper Conductor

Cadmium copper conductors are copper alloys containing a small percentage of cadmium to improve strength. They provide better mechanical properties than pure copper while maintaining good conductivity. These conductors are used where moderate strength and good electrical performance are required. They are suitable for medium-span transmission lines.
8. Phosphor Bronze Conductor

Phosphor bronze conductors are copper-tin alloys known for high tensile strength and corrosion resistance. They have lower conductivity than copper but excellent mechanical durability. These conductors are mainly used in coastal areas, railway electrification, and telecommunication lines. They are suitable for conditions requiring high strength and corrosion resistance.
9. Zinc-Coated Steel Conductor (Shield Wire)

Zinc-coated steel conductors are mainly used as shield wires or earth wires above transmission lines. They protect the line from lightning strokes by diverting surges safely to ground. These conductors have very high mechanical strength but do not carry power current. Their main function is protection rather than power transmission.
10. Bundled Conductors (for Extra High Voltage Lines)
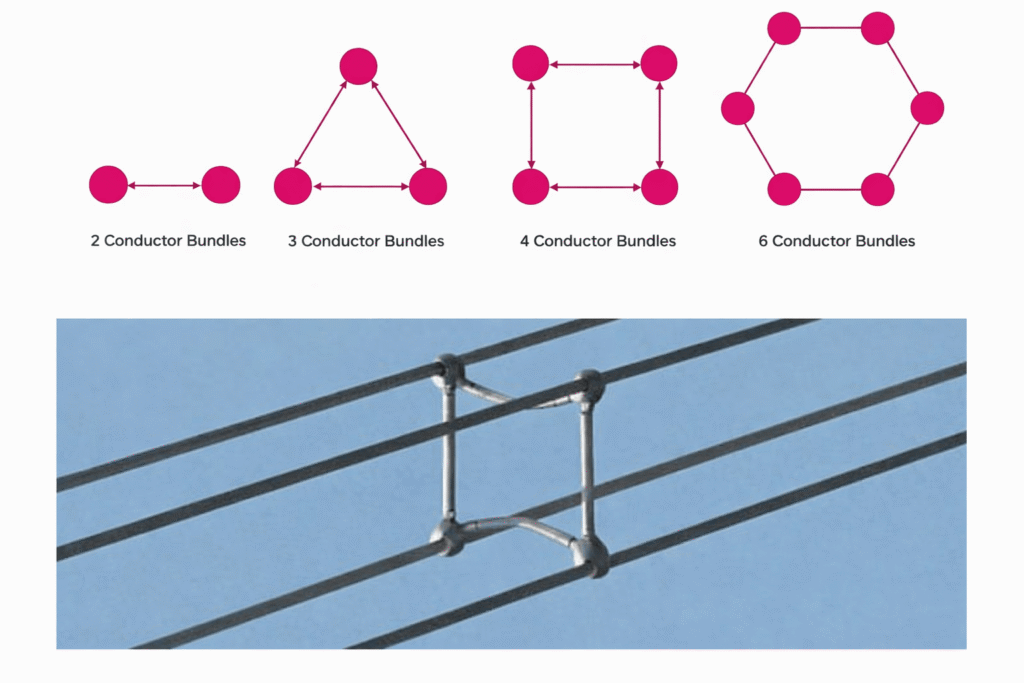
Bundled conductors consist of two or more sub-conductors per phase separated by spacers. They are used in Extra High Voltage (EHV) and Ultra High Voltage (UHV) transmission lines. Bundling reduces corona loss, radio interference, and line reactance. It improves transmission efficiency and stability for long-distance power transfer.
Use-Based Classification
1. For Short Spans and Urban Areas
- Hard-Drawn Copper
- AAC
2. For Medium Spans and Corrosive Areas
- AAAC
3. For Long Spans and High Voltage Lines
- ACSR
- ACAR
4. For Shielding and Support
- Galvanized Steel (Earth wire)
5. For Extra High Voltage (EHV) Lines
- Bundled Conductors
Selection Criteria of Conductors (Factors)
- Current Carrying Capacity
- The conductor must safely carry the maximum load current.
- Electrical Conductivity
- High conductivity reduces resistance and power loss.
- Mechanical Strength
- Conductor must withstand wind, ice, and self-weight.
- Voltage Drop
- Voltage drop should be within permissible limits..
- Power Loss
- Low resistance reduces I²R losses.
- Improves transmission efficiency.
- Thermal Performance
- Conductor must dissipate heat effectively.
- Environmental Conditions
- Weather conditions influence conductor choice.
- Cost and Economy
- Aluminium is economical for long distances.
Comparison Chart of Transmission Line Conductors
| Conductor | Conductivity | Mechanical Strength | Weight | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDC | Very High | Medium | Heavy | Short spans, special lines |
| AAC | High | Low | Light | Urban, short-span lines |
| AAAC | Medium | High | Light | Coastal, medium spans |
| ACSR | Medium | Very High | Medium | Long-span, high-voltage lines |
| ACAR | High | High | Medium | High-capacity transmission |
