Introduction
In long transmission lines operating at high voltage and light load or no-load condition, it is observed that the receiving-end voltage becomes greater than the sending-end voltage. This unusual rise in voltage at the receiving end is known as the Ferranti Effect.
Ferranti effect is an important phenomenon in long and extra-high voltage transmission lines, especially under light load conditions, and must be considered in power system design and voltage regulation.
What is Ferranti Effect?
Ferranti effect is the phenomenon in which the receiving-end voltage of a long transmission line becomes higher than the sending-end voltage when the line is lightly loaded or open-circuited.
Mathematically:
where:
= Receiving end voltage
= Sending end voltage
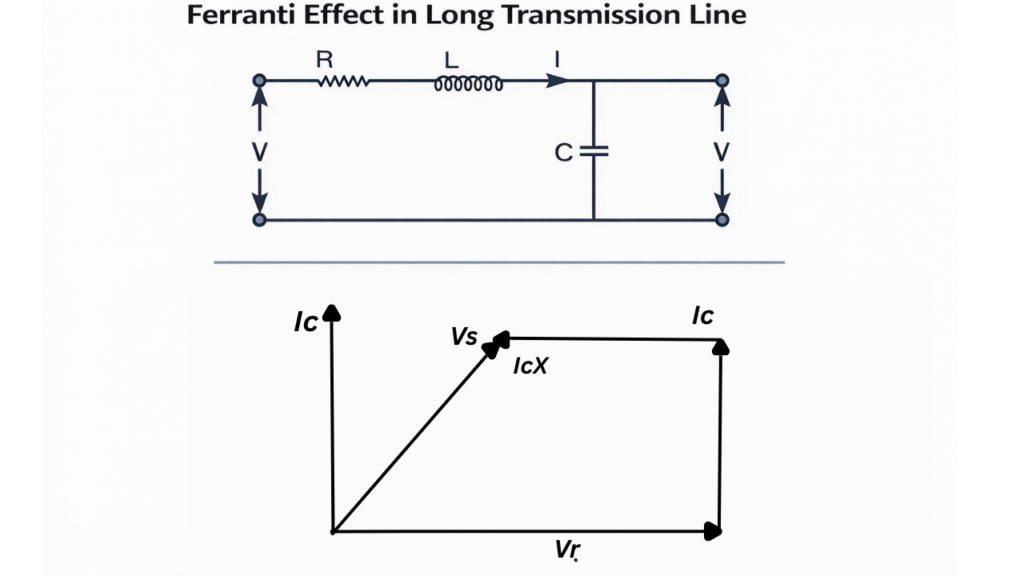
Cause of Ferranti Effect
Ferranti effect occurs mainly due to the capacitance of the transmission line.
In long transmission lines:
- The line has distributed capacitance between conductors and earth
- When the line is lightly loaded or open-circuited, charging current flows through this capacitance
- This charging current leads the voltage by 90°
- The reactive voltage drop across the line inductance becomes negative
As a result, the receiving-end voltage increases and becomes greater than the sending-end voltage.
Physical Explanation
- Under light load or no-load condition, line current is very small
- The dominant current is the charging current due to line capacitance
- This charging current produces a voltage rise across the inductance of the line
- The voltage rise adds to the receiving-end voltage
Hence:
This causes to become greater than .
Conditions for Ferranti Effect
Ferranti effect becomes significant under the following conditions:
- Long transmission lines (generally length > 150 km)
- High operating voltage
- Light load or no-load condition
- Lines having large capacitance
Short and medium lines show negligible Ferranti effect.
Effects of Ferranti Effect
Ferranti effect produces the following problems:
- Over-voltage at receiving end
- Stress on insulation
- Possibility of insulation breakdown
- Poor voltage regulation
- Damage to equipment connected at receiving end
Hence, it must be properly controlled in long EHV lines.
Methods of Reducing Ferranti Effect
To control the rise in receiving-end voltage, the following methods are used:
1. Use of Shunt Reactors
Shunt reactors are connected at the receiving end or along the line.
- They absorb reactive power
- Neutralize the effect of line capacitance
- Reduce the charging current
- Control the voltage rise
This is the most effective method.
2. Operating Line Under Load
When the line carries sufficient load:
- Line current increases
- Effect of capacitance reduces
- Ferranti effect becomes negligible
3. Use of Series Compensation
Series reactors or inductors can be used to balance capacitive effects and limit voltage rise.
4. Switching Control and Voltage Regulation
Proper switching strategy and voltage regulators are used to maintain voltage within limits during light load conditions.
