Introduction
Solar energy has become one of the most important renewable energy sources in modern power systems. With increasing demand for clean and sustainable electricity, different types of solar power plants are being developed and installed across the world. Each type of solar power plant uses a different technology to convert sunlight into electrical energy.
This article explains the major types of solar power plants, their working principles, advantages, limitations, and typical applications.
What is Solar Power?
Solar power is the energy obtained from sunlight and converted into electrical or thermal energy using suitable technologies such as solar photovoltaic cells or solar thermal collectors. The sun provides an enormous amount of energy to the earth every day, making solar power an unlimited and clean source of energy.
Working Principle of Solar Power
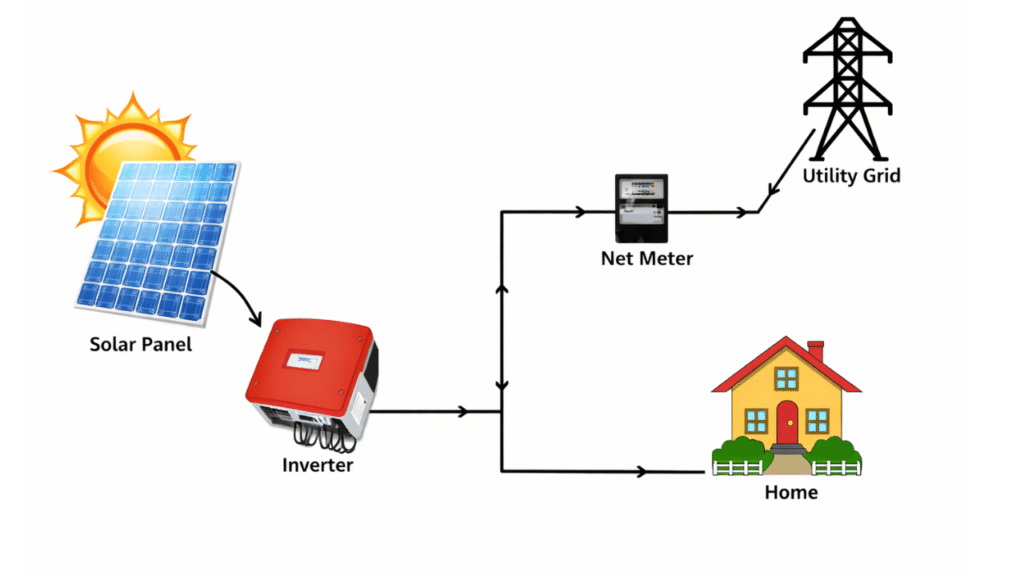
The solar plant system, a Photovoltaic (PV) power plant, is a large-scale system designed to generate electrical energy from sunlight. This type of power plant utilises solar energy to produce electricity, making it a conventional power plant. The components of a solar power plant model include panels, inverters, and other support systems that convert the sun’s energy into electricity.
A solar power plant for homes can be harnessed to generate electrical energy using solar photovoltaic panels or concentrated solar energy. Solar PV panels directly convert the energy of the sun’s radiation into electricity, which is included in solar power plant information.
Photovoltaic Principle
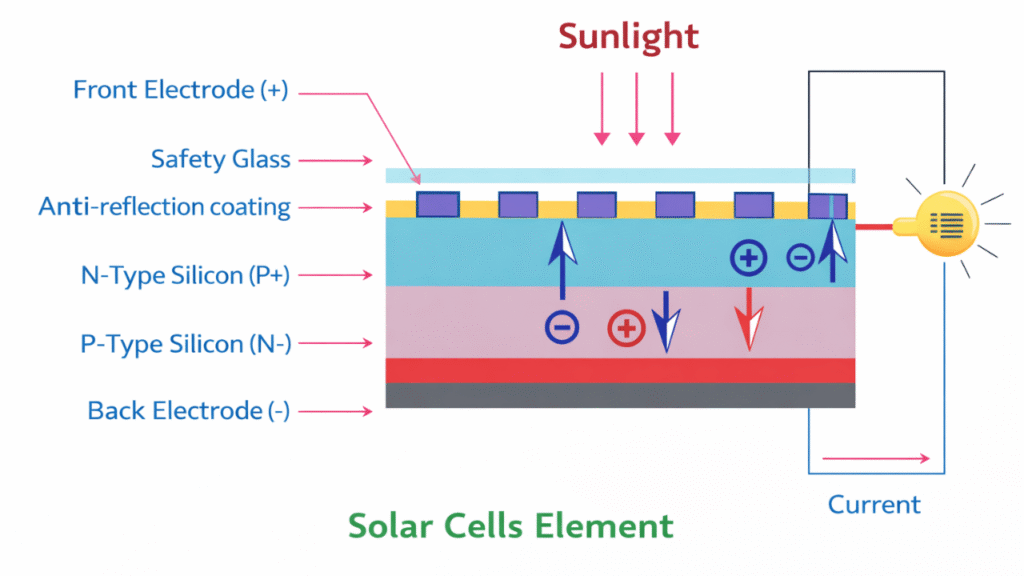
In the photovoltaic method, electrical energy is generated directly from sunlight using semiconductor materials, commonly silicon.
When sunlight falls on the surface of a solar cell, photons strike the semiconductor atoms and transfer their energy to the valence electrons. As a result, electrons gain sufficient energy to break free from their atomic bonds and move into the conduction band.
Due to the presence of a PN junction inside the solar cell, an internal electric field is created. This electric field drives the free electrons in one direction and holes in the opposite direction, establishing a direct current (DC) at the output terminals.
Thus, the photovoltaic effect enables the direct conversion of solar energy into electrical energy without any moving parts.
Solar Thermal Principle
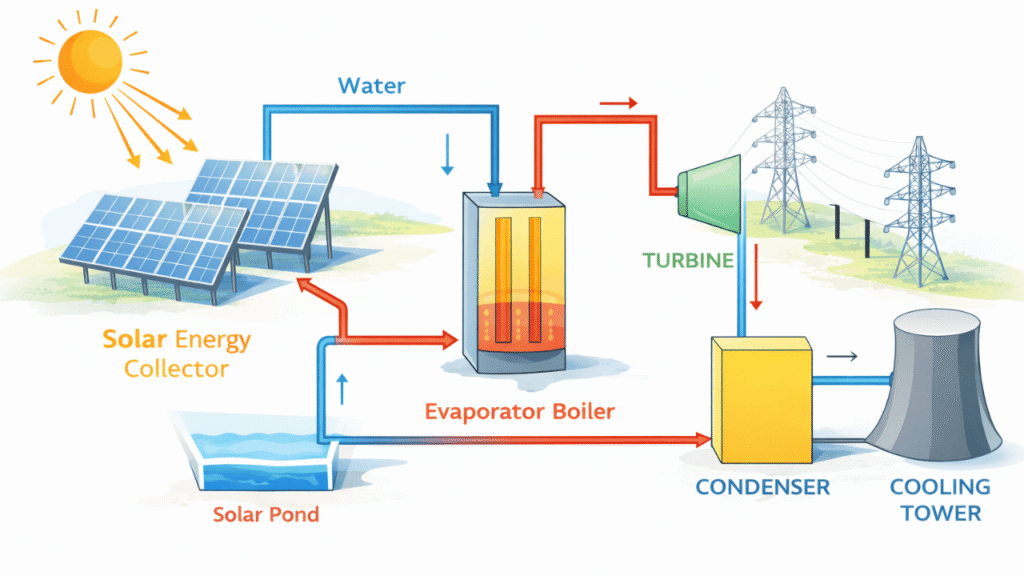
In solar thermal power generation, sunlight is first converted into heat energy and then into electrical energy.
Solar radiation is concentrated or absorbed by special collectors or mirrors to produce high-temperature heat. This heat is used to convert water into high-pressure steam. The steam is then directed onto a steam turbine, causing it to rotate. The rotating turbine drives an electrical generator, which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
This method follows the same working principle as conventional thermal power plants, with solar energy replacing fossil fuels as the heat source.
Main Components of a Solar Power System
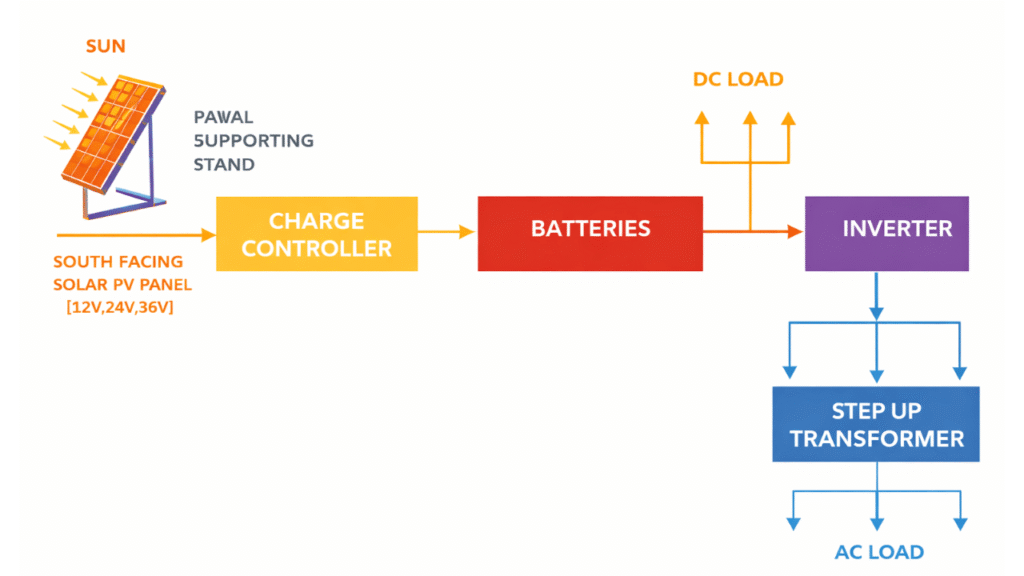
A solar power system consists of several essential components that work together to convert sunlight into usable electrical energy and deliver it to loads or the utility grid.
- Solar Panel
The solar panel is the primary component of a solar power system. It is made up of many solar cells connected in series and parallel. When sunlight falls on the panel, the photovoltaic effect generates direct current (DC) electricity. The amount of power produced depends on solar intensity, panel efficiency, and surface area.
- Charge Controller
The charge controller regulates the flow of electrical energy between the solar panels, batteries, and load. Its main function is to protect the batteries from overcharging and deep discharging. It maintains proper battery voltage and improves battery life by controlling charging and discharging cycles.
- Battery (Optional)
The battery stores excess electrical energy generated during sunlight hours. This stored energy is used when sunlight is unavailable, such as at night or during cloudy conditions. Batteries provide continuous and reliable power supply in off-grid and hybrid solar systems.
- Inverter
The inverter converts the DC power produced by the solar panels or batteries into alternating current (AC). Since most household and industrial appliances operate on AC supply, the inverter is a critical component for making solar energy usable in practical applications.
- Transformer
The transformer steps up the AC voltage produced by the inverter to a higher level suitable for transmission and distribution. This reduces power losses during long-distance transmission and allows proper integration with the utility grid.
- Grid Connection System
The grid connection system connects the solar power plant to the utility grid. It allows excess generated power to be exported to the grid and enables power import from the grid when solar generation is insufficient. This system ensures stable and continuous power supply.
Types of Solar Power Systems
Solar power systems are classified based on their connection with the utility grid and the presence of energy storage systems. The three main types are grid-connected, off-grid, and hybrid solar systems.
1. Grid-Connected Solar System
A grid-connected solar system is directly connected to the utility electricity grid. The electricity generated by the solar panels is first converted into AC by the inverter and then supplied to the grid and local loads.
When solar generation exceeds the local demand, the surplus energy is exported to the grid through a net metering system. During periods of insufficient sunlight, electricity is drawn from the grid.
Features:
- No battery storage required
- High efficiency and low installation cost
- Continuous power availability through grid support
Applications:
- Residential rooftops
- Commercial buildings
- Industrial solar plants
2. Off-Grid Solar System
An off-grid solar system operates independently of the utility grid. It uses battery banks to store excess energy generated during the day. The stored energy is used at night or during low-sunlight conditions.
This system is suitable for areas where grid supply is unavailable or unreliable.
Features:
- Complete energy independence
- Requires battery storage system
- Higher initial cost due to batteries
Applications:
- Remote villages
- Rural electrification
- Telecommunication stations
- Isolated homes
3. Hybrid Solar System
A hybrid solar system combines solar panels, battery storage, and grid or diesel backup. It offers the advantages of both grid-connected and off-grid systems.
During normal operation, solar energy supplies the load and charges the batteries. Excess power can be exported to the grid. In case of power failure or low solar generation, batteries or diesel generators provide backup power.
Features:
- High reliability and uninterrupted supply
- Efficient energy management
- Flexible operation modes
Applications:
- Hospitals
- Data centers
- Commercial complexes
- Critical power systems
Difference Between Types of Solar Power Systems
Solar power systems are mainly classified into Grid-Connected, Off-Grid, and Hybrid systems based on their grid connectivity and energy storage arrangement. The main differences are explained below.
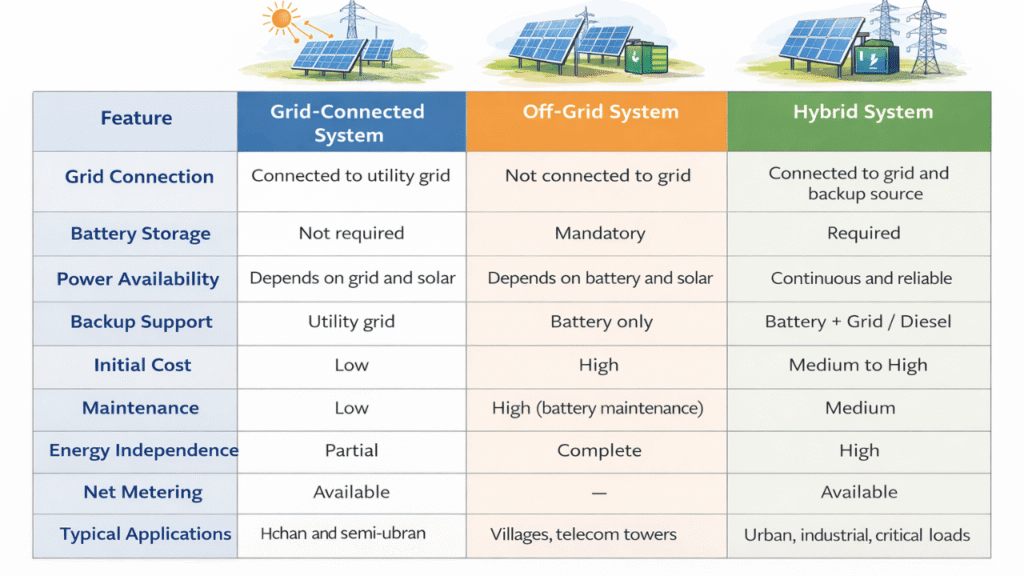
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of solar power systems is essential for selecting the right solution for efficient and sustainable energy generation. Grid-connected solar systems are ideal for reducing electricity bills in urban areas, while off-grid solar systems provide reliable power in remote locations without utility access. Hybrid solar systems offer the best of both worlds by combining solar energy, battery storage, and grid or backup support to ensure uninterrupted power supply.
Short FAQ – Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR)
What are the main types of solar power systems?
The main types of solar power systems are grid-connected, off-grid, and hybrid solar systems. Each type differs in grid connection, battery usage, and power reliability.
Which solar power system is best for homes?
Grid-connected solar systems are best for homes in urban areas because they are cost-effective, require no batteries, and allow net metering to reduce electricity bills.
Do grid-connected solar systems work during power cuts?
No, grid-connected solar systems stop working during power cuts for safety reasons unless they are combined with battery backup or hybrid configuration.
