What is an Electric Motor?
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. This conversion takes place due to the interaction between the magnetic field and current-carrying conductors, producing a force according to Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule.
Electric motors are preferred over other prime movers because they are clean, efficient, reliable, and easy to control. Depending on the type of electrical supply, construction, and application, electric motors are classified into different categories.
Classification of Electric Motors
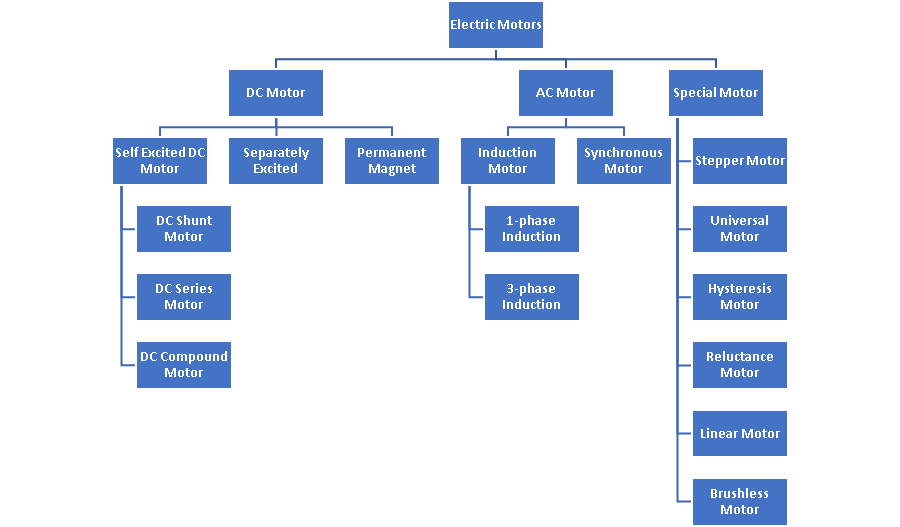
AC Motor
AC motors are electric motors that operate on alternating current (AC) supply. They are widely used in domestic, commercial, and industrial applications due to their simple construction, high efficiency, ruggedness, and low maintenance. AC motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy using the principle of a rotating magnetic field.
The AC motors are further classified into two types:
- Asynchronous or Induction Motor
- Synchronous Motor
Induction Motor
An induction motor, also known as an asynchronous motor, is an AC electric motor in which the rotor current is produced by electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current flows through the stator winding, it produces a rotating magnetic field. This rotating field induces current in the rotor conductors.
Due to the interaction between the rotor current and the stator magnetic field, torque is produced, causing the rotor to rotate. The rotor speed is always less than the synchronous speed, which is why it is called an asynchronous motor. Induction motors are widely used because of their simple construction, low cost, and minimal maintenance.
Induction motors are classified into two types:
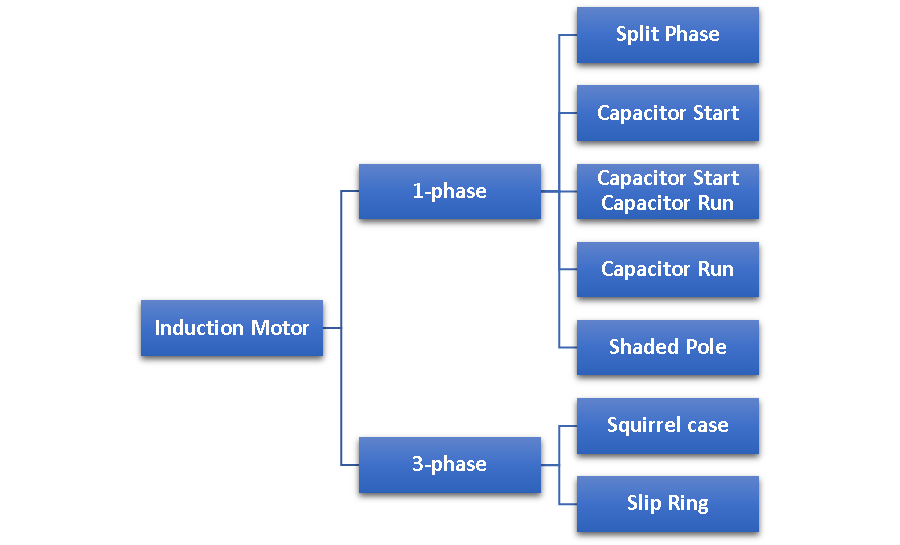
Single Phase Induction Motor
A single phase induction motor is an AC motor that operates on a single-phase AC supply. It is widely used in domestic and light commercial applications where three-phase power is not available. These motors are simple in construction, reliable, and economical.
Unlike three-phase induction motors, a single phase induction motor is not self-starting and requires a starting mechanism to begin rotation.
Types of Single Phase Induction Motors:
- Split Phase Induction Motor
- Capacitor Start Induction Motor
- Capacitor Start Capacitor Run Motor
- Capacitor Run Induction Motor
- Shaded Pole Induction Motor
Split Phase Induction Motor
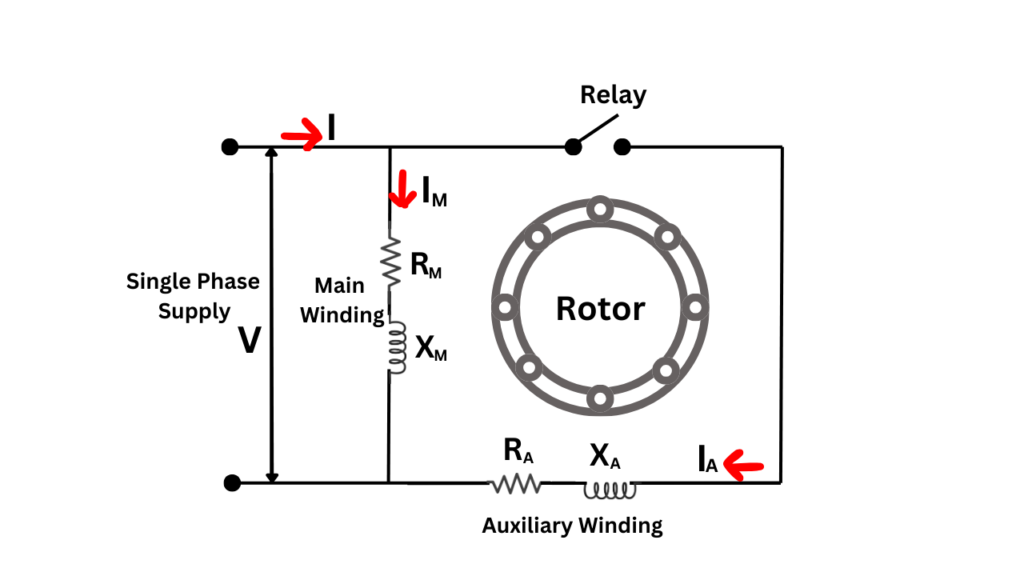
A single phase supply by itself produces only an alternating magnetic field, which cannot start a motor. To solve this problem, split phase motors use an extra winding called the auxiliary or starting winding to create a small phase difference and generate starting torque.
Applications of Split Phase Induction Motor:
- Washing machines
- Small water pumps
- Fans and blowers
- Office equipment
- Light domestic appliances
Capacitor Start Induction Motor
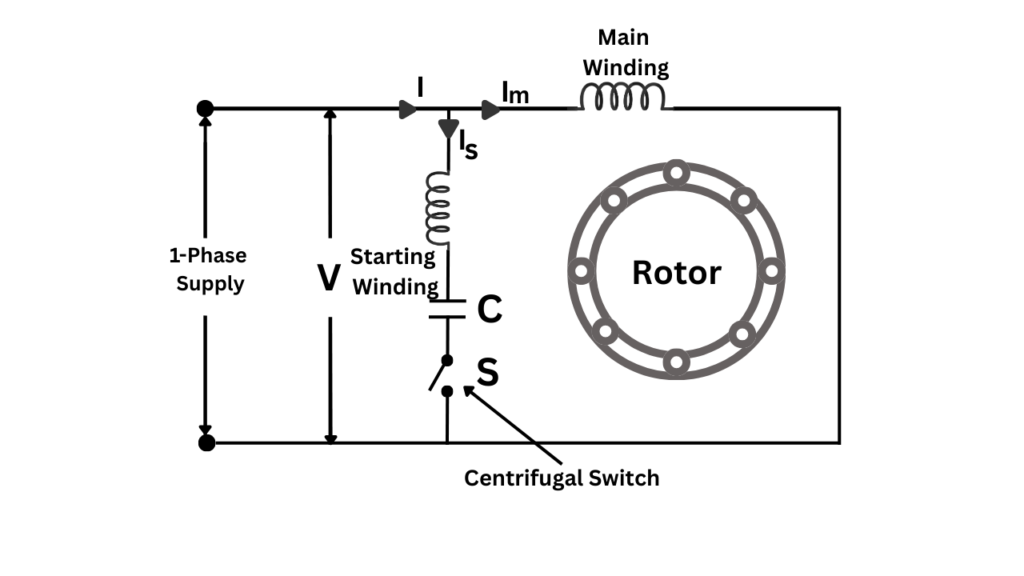
A capacitor start induction motor is a single-phase motor that uses a large value capacitor to improve starting torque. The capacitor creates a large phase difference between the currents in the main winding and starting winding, producing a strong rotating magnetic field.
An electrolytic capacitor of short-time duty is connected in series with the starting winding through a centrifugal switch. When the motor reaches about 75% of synchronous speed, the starting winding and capacitor are disconnected. These motors are used in applications requiring high starting torque, such as refrigerators and compressors.
Applications of Capacitor Start Induction Motor:
- Refrigerators
- Air compressors
- Water pumps
- Air conditioners
- Conveyors
Capacitor Start Capacitor Run Motor
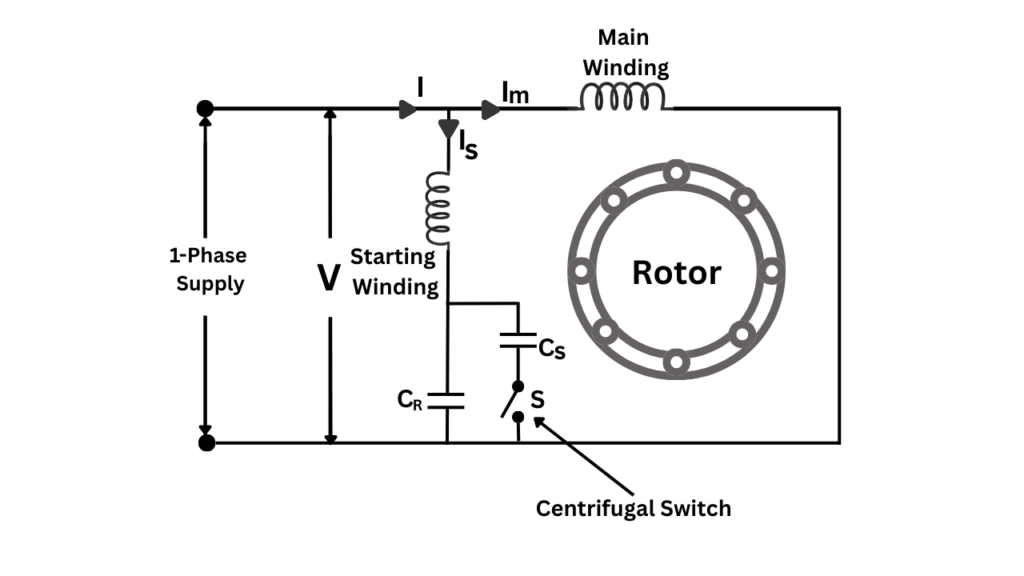
A Capacitor Start Capacitor Run Motor is a single-phase induction motor that uses two capacitors one for starting and one for running to achieve high starting torque and smooth, efficient operation during running conditions.
Unlike a capacitor start motor, the run capacitor remains connected even after the motor reaches rated speed, which improves power factor, efficiency, and torque characteristics.
Applications of Capacitor Start Capacitor Run Motor:
- Air conditioners
- Refrigeration units
- Air compressors
- Water pumps
- Conveyors
- HVAC systems
Capacitor Run Induction Motor
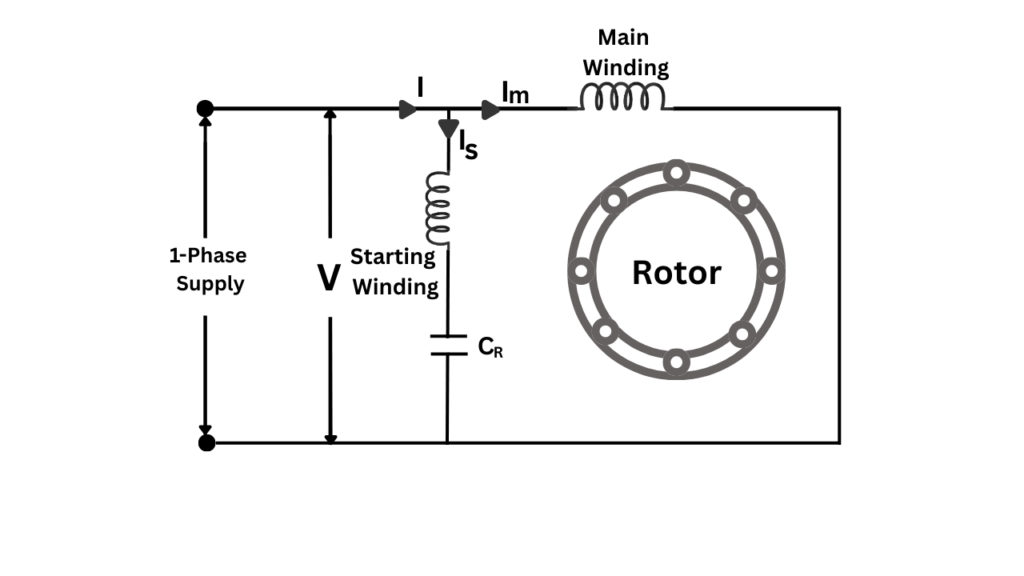
A Capacitor Run Induction Motor, also known as a Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) Motor, is a single-phase induction motor in which a capacitor remains permanently connected in series with the auxiliary winding during both starting and running conditions.
Unlike capacitor start motors, no centrifugal switch is used, making the motor more reliable and quieter.
Applications of Capacitor Start Capacitor Run Motor:
- Ceiling and table fans
- Blowers
- Exhaust fans
- Room air coolers
- Office equipment
- Small pumps
Shaded Pole Induction Motor
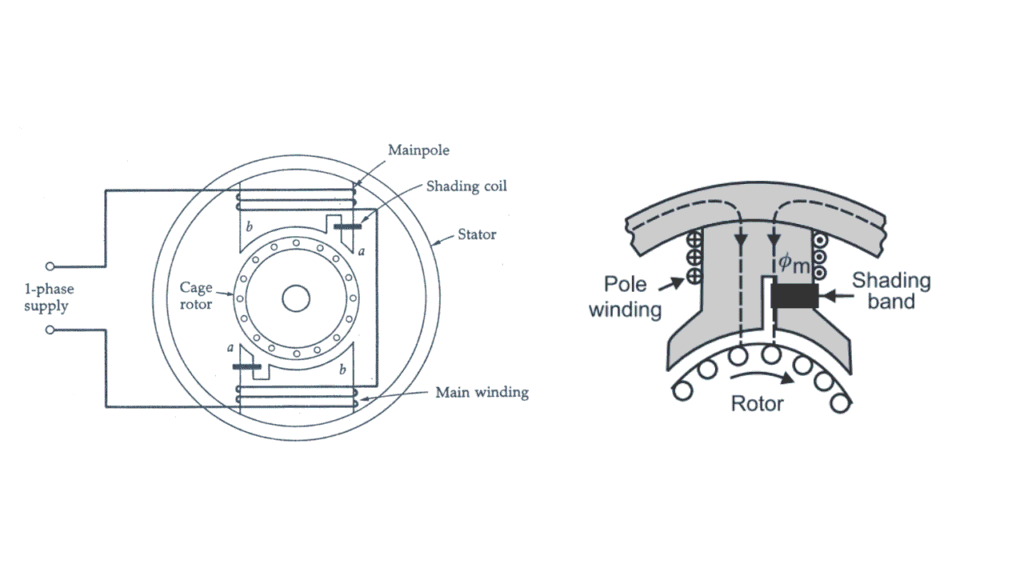
A Shaded Pole Induction Motor is the simplest type of single-phase induction motor. It is widely used in low-power applications where low starting torque, simple construction, and low cost are acceptable.
This motor uses a shading coil (shading band) to produce a weak rotating magnetic field, allowing the motor to start without any auxiliary winding or capacitor.
Applications of Shaded Pole Induction Motor
Due to low starting torque, shaded pole motors are used only in light-duty applications, such as:
- Table fans
- Exhaust fans
- Electric clocks
- Hair dryers
- Small blowers
- Refrigerator evaporator fans
Synchronous Motor
A synchronous motor is an AC motor that runs at a constant speed, known as synchronous speed, which depends only on the supply frequency and the number of poles. Unlike induction motors, the rotor of a synchronous motor rotates in step with the rotating magnetic field of the stator, meaning there is no slip.
Synchronous Speed-
The synchronous speed of a motor is given by:
Where:
- = synchronous speed (rpm)
- = supply frequency (Hz)
- = number of poles
Because of this property, synchronous motors are widely used in applications where constant speed and power factor control are required.
DC Motor
A DC motor is an electrical machine that converts direct current (DC) electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works on the fundamental principle that a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experiences a mechanical force. This force produces torque, causing the motor shaft to rotate.
Separately Excited DC Motor
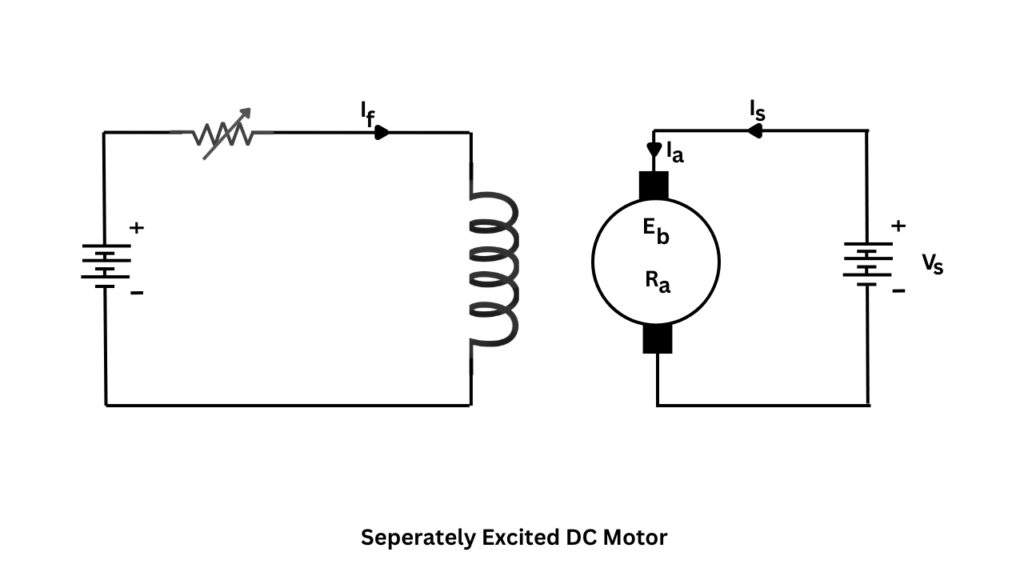
A separately excited DC motor is a type of DC motor in which the field winding is energized by an independent DC source, separate from the armature supply. Because the field current is not affected by armature current, this motor offers excellent speed control and stable operation.
Applications of Separately Excited DC Motor
These motors are used where precise speed control is essential, such as:
- Steel rolling mills
- Paper and textile industries
- Machine tools
- Elevators
- Laboratory testing equipment
Self-Excited DC Motor
A self-excited DC motor is a DC motor in which the field winding is energized by the same DC supply that feeds the armature. Unlike a separately excited DC motor, no external power source is required for field excitation.
These motors are widely used because of their simple construction, good speed regulation, and reliability.
Shunt DC Motor
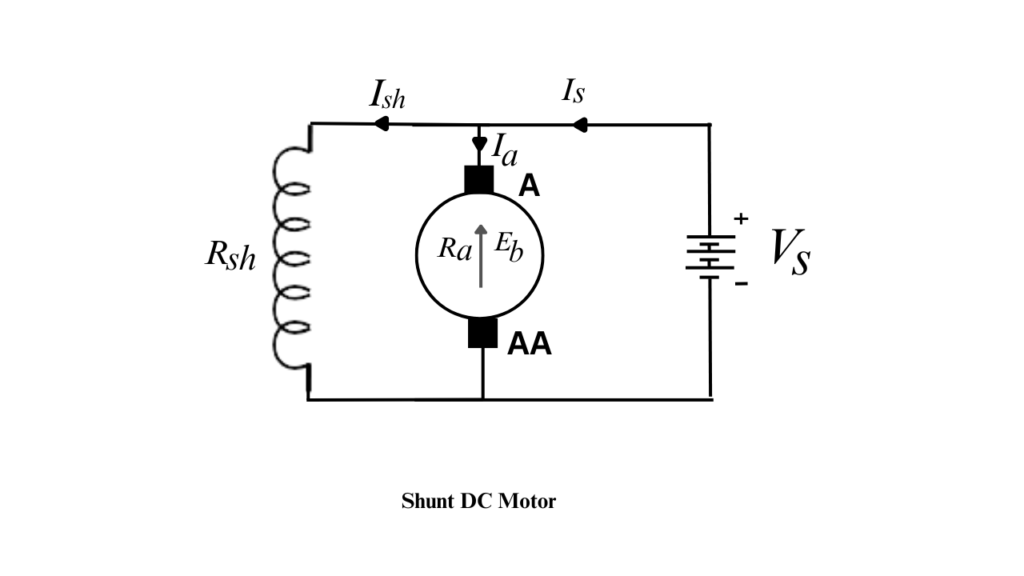
A Shunt DC Motor is a type of self-excited DC motor in which the field winding is connected in parallel (shunt) with the armature winding. Because the field current remains nearly constant, a shunt DC motor operates at an almost constant speed, making it suitable for constant-speed applications.
Applications of Shunt DC Motor
Shunt DC motors are used where constant speed is required, such as:
- Machine tools
- Lathes
- Fans and blowers
- Centrifugal pumps
- Conveyors
- Printing presses
Series DC Motor
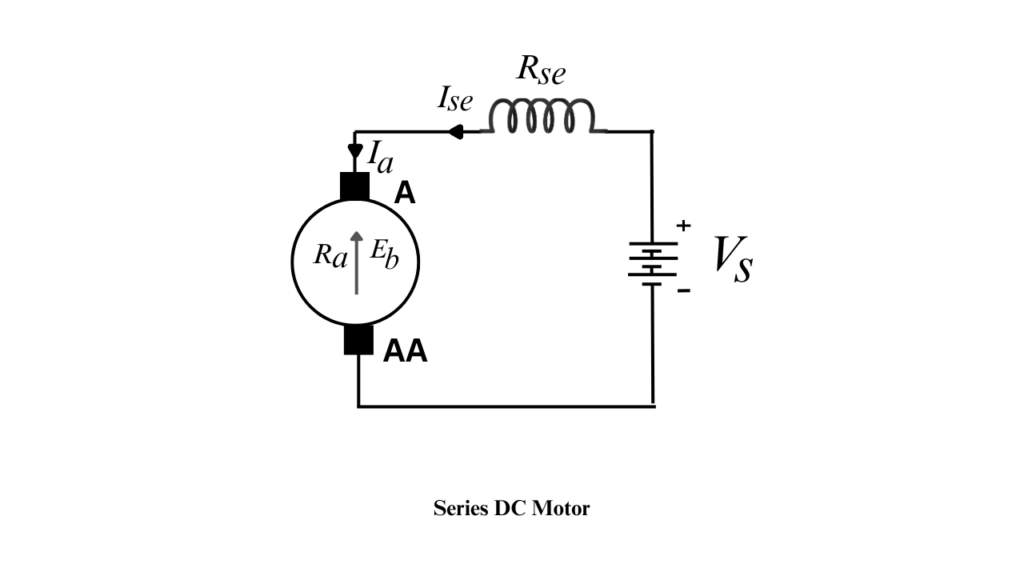
A Series DC Motor is a type of self-excited DC motor in which the field winding is connected in series with the armature winding. As a result, the same current flows through both the armature and the field winding. This motor is known for its very high starting torque, making it suitable for heavy starting loads.
Applications of Series DC Motor
Because of its high starting torque, series DC motors are used in:
- Electric traction (locomotives, trams)
- Cranes and hoists
- Elevators
- Winches
- Rolling mills
Compound DC Motor
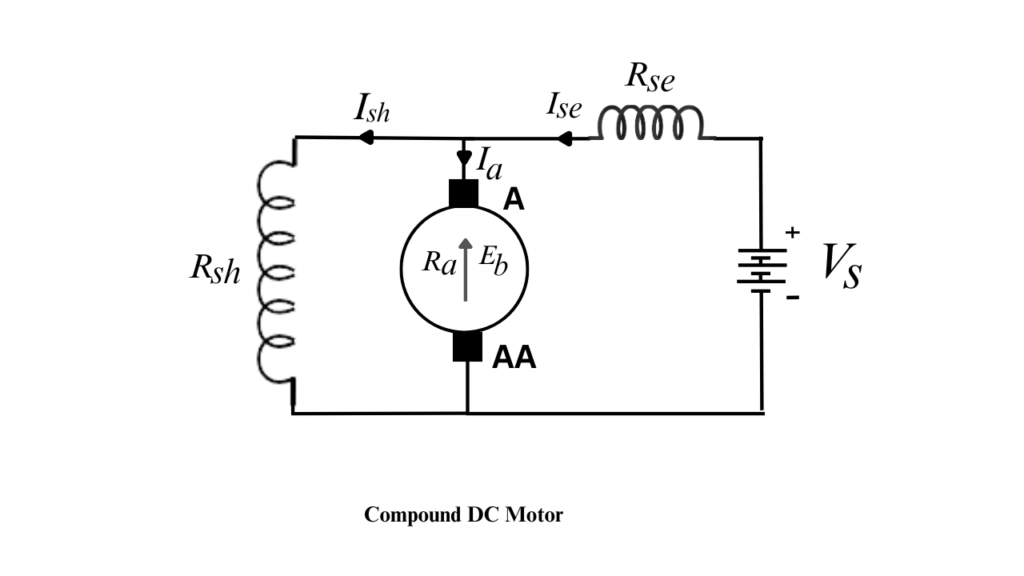
A Compound DC Motor is a type of self-excited DC motor that combines the characteristics of both shunt and series DC motors. It contains two field windings:
- a shunt field winding connected in parallel with the armature, and
- a series field winding connected in series with the armature.
Because of this combination, a compound DC motor offers high starting torque along with better speed regulation.
The compound motor can be further subdivided as:
- Cumulative compound motors
- Differential compound motors
Applications of Compound DC Motor
Compound DC motors are used where both high starting torque and good speed regulation are required, such as:
- Elevators
- Rolling mills
- Presses and shears
- Conveyors
- Heavy-duty pumps
Types of Special Motors
Stepper Motor
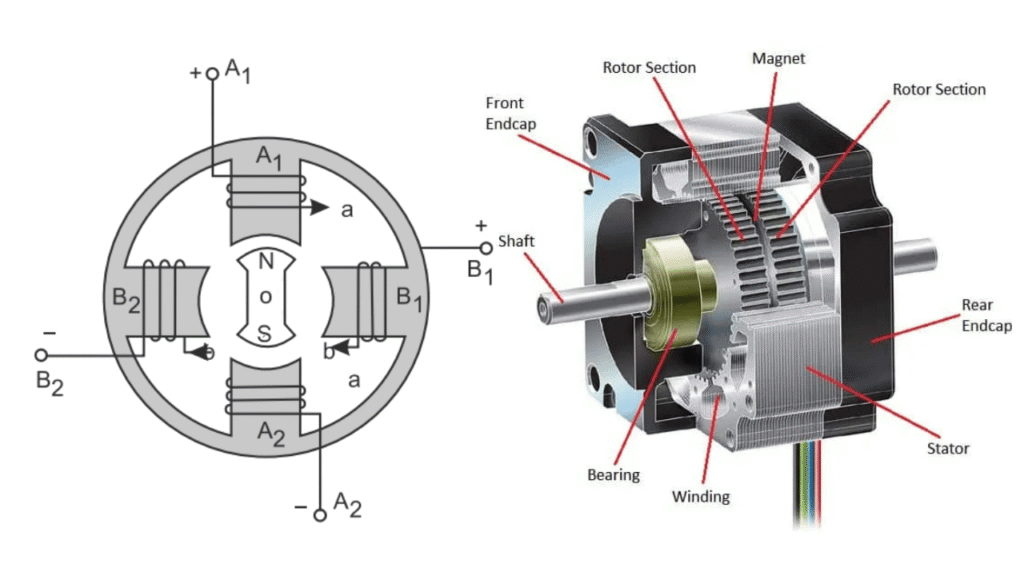
A stepper motor is a special type of electric motor that converts electrical pulses into precise mechanical movement. Unlike conventional motors that rotate continuously, a stepper motor rotates in discrete steps, allowing accurate control of position, speed, and direction without the need for feedback devices.
Applications of Stepper Motor:
- CNC machines
- 3D printers
- Robotics
- Printers and scanners
- Camera positioning systems
- Medical equipment
Universal Motor
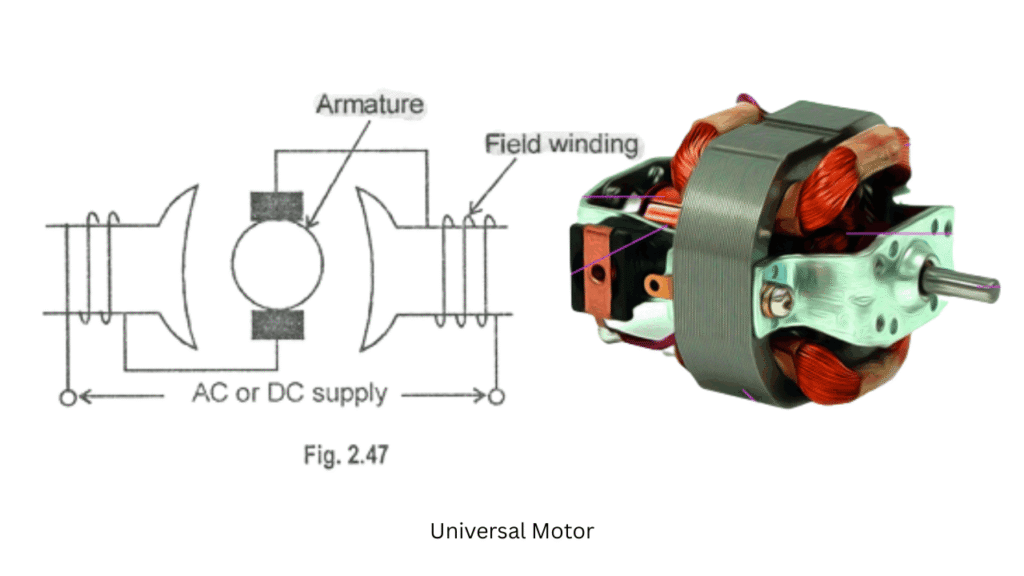
A universal motor is a special type of electric motor that can operate on both AC and DC supply. It is essentially a series-wound DC motor modified to run on AC power. Because of its very high speed and high starting torque, the universal motor is widely used in portable household and industrial appliances.
Applications of Universal Motor:
- Mixers and grinders
- Vacuum cleaners
- Hair dryers
- Electric drills
- Sewing machines
- Portable power tools
Hysteresis Motor
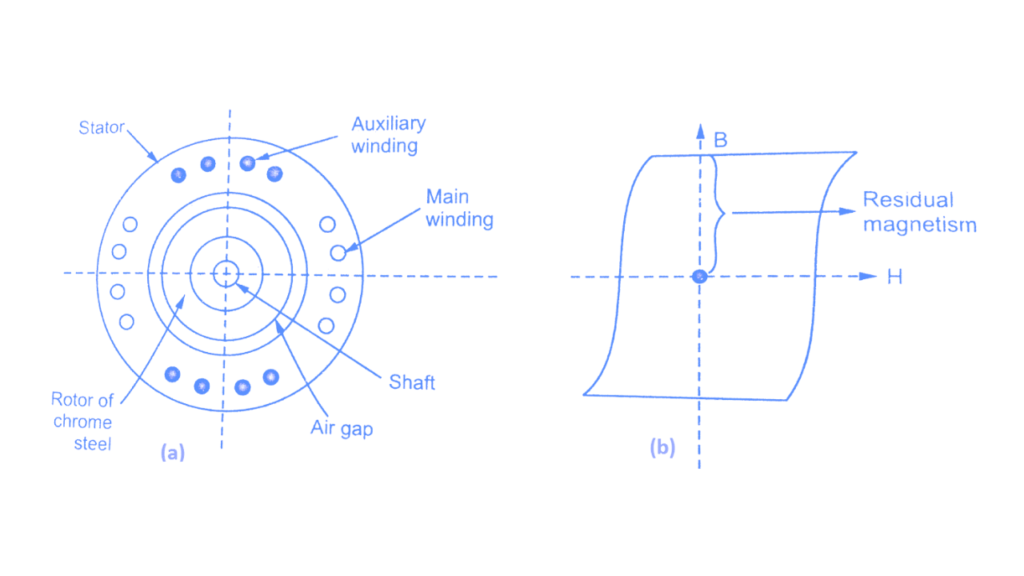
A hysteresis motor is a special type of single-phase synchronous motor that operates on the principle of magnetic hysteresis loss. It is known for its smooth, quiet operation and constant speed, making it ideal for precision and timing applications.
Applications of Hysteresis Motor
Hysteresis motors are used where constant speed and quiet operation are essential:
- Electric clocks
- Timing devices
- Record players
- Audio equipment
- Instrumentation
- Teleprinters
Reluctance Motor
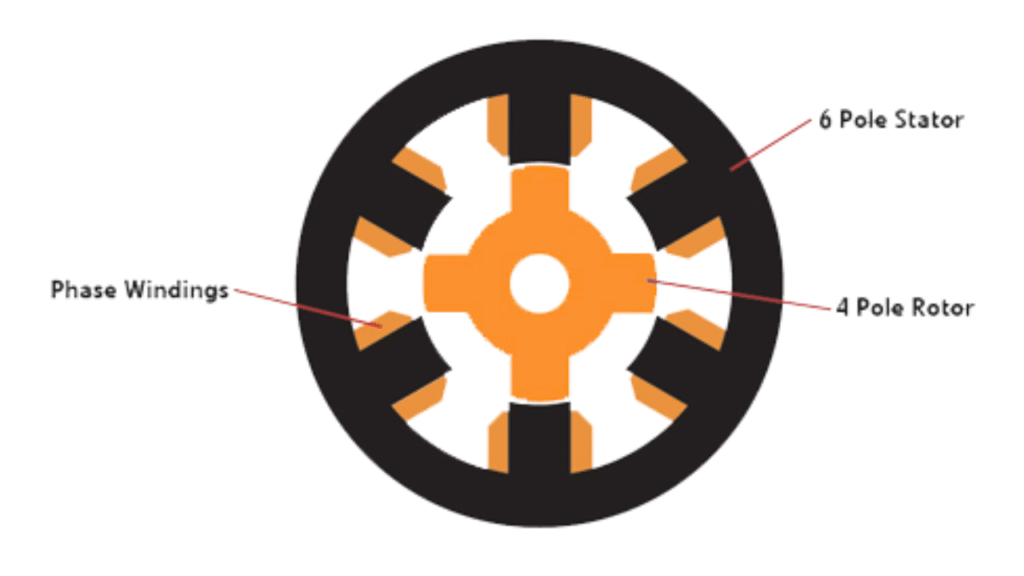
A reluctance motor is a type of single-phase or three-phase synchronous motor that operates on the principle of minimum reluctance. In this motor, torque is produced because the rotor tends to align itself along the path of lowest magnetic reluctance created by the stator magnetic field.
Applications of Reluctance Motor
Reluctance motors are used where constant speed and low cost are important:
- Electric clocks
- Timing devices
- Recording instruments
- Control equipment
- Small fans and blowers
Linear Motor
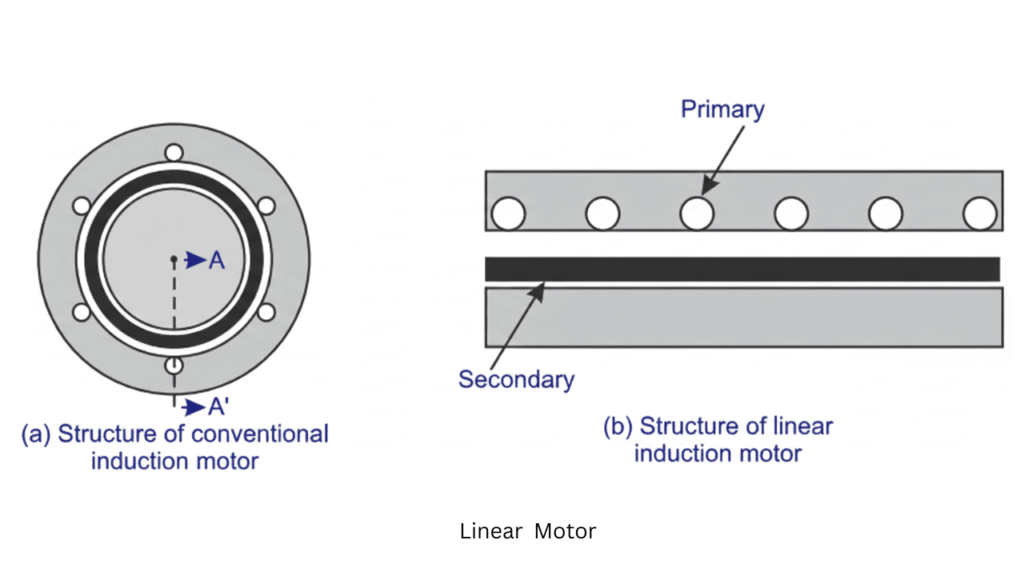
A linear motor is an electric motor that produces linear motion directly, instead of rotational motion. It works on the same electromagnetic principles as conventional motors, but the stator and rotor are cut open and laid flat, resulting in straight-line movement.
Applications of Linear Motor
Linear motors are widely used in modern and high-precision systems:
- Maglev trains
- CNC machines
- Robotic actuators
- Automatic sliding doors
- Conveyor systems
- Elevator systems
- Semiconductor manufacturing
Brushless Motor (BLDC Motor)
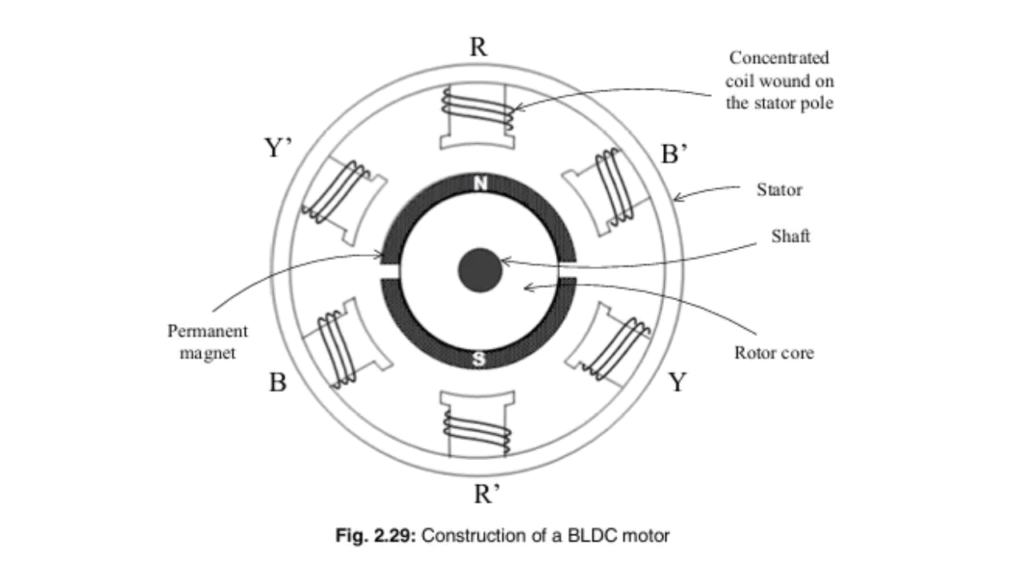
A brushless motor, commonly called a Brushless DC Motor (BLDC motor), is an electric motor that operates without brushes and a commutator. Instead of mechanical commutation, it uses electronic commutation to control current flow in the motor windings. This results in higher efficiency, longer life, and lower maintenance compared to brushed motors.
Applications of Brushless Motor
Brushless motors are widely used in modern electrical and electronic systems:
- Electric vehicles (EVs)
- Computer cooling fans
- Drones and UAVs
- Washing machines
- Air conditioners
- CNC machines
- Medical equipment
